- Save resources and time.
- Monitor one's business processes as a whole.
- Improves productivity for employees.
- Customer Experience Enhancement.
- Make better choices.
- Raising revenue.
- Freedom to view details on any computer from anywhere, at any time.
- Automating processes that can increase the level of services rendered by a company and the needs for human intervention.
- As the number of linked devices grows as more knowledge is exchanged between devices, there is often a growing opportunity for a hacker to capture sensitive information.
- Enterprises will potentially have to work with large amounts — maybe even millions — of IoT devices and it would be difficult to gather and handle data from all of those devices.
- When there's a network error, any linked computer is likely to get infected.
- Since there is no universal IoT interface standard, products from various vendors may have trouble interacting with one another.
folder_open MagRabbit-AU News
Real-life uses of the Internet of Things in the Digital Age
Introduction
One thing in the Internet of Things can be a person with a heart monitor implant, a farm animal with a biochip transponder, an automobile that has built-in sensors to alert the driver when the tire pressure is low or any other natural or man-made object that can be assigned an Internet Protocol (IP) address and can transfer data over a network.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a collection of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines with unique identifiers (UIDs) and the ability to transmit data across a network without human contact.
Due to the convergence of multiple technologies, real-time analytics, machine learning, commodity sensors, and embedded systems, the definition of the Internet of Things has evolved. Traditional fields of embedded systems, wireless sensor networks, control systems, automation (including home and building automation), and others all contribute to the Internet of Things.
In the consumer market, IoT technology is most synonymous with products that support one or more common ecosystems and can be controlled via devices associated with that ecosystem, such as smartphones and smart speakers, such as lighting fixtures, thermostats, home security systems and cameras and other home appliances.
IoT system
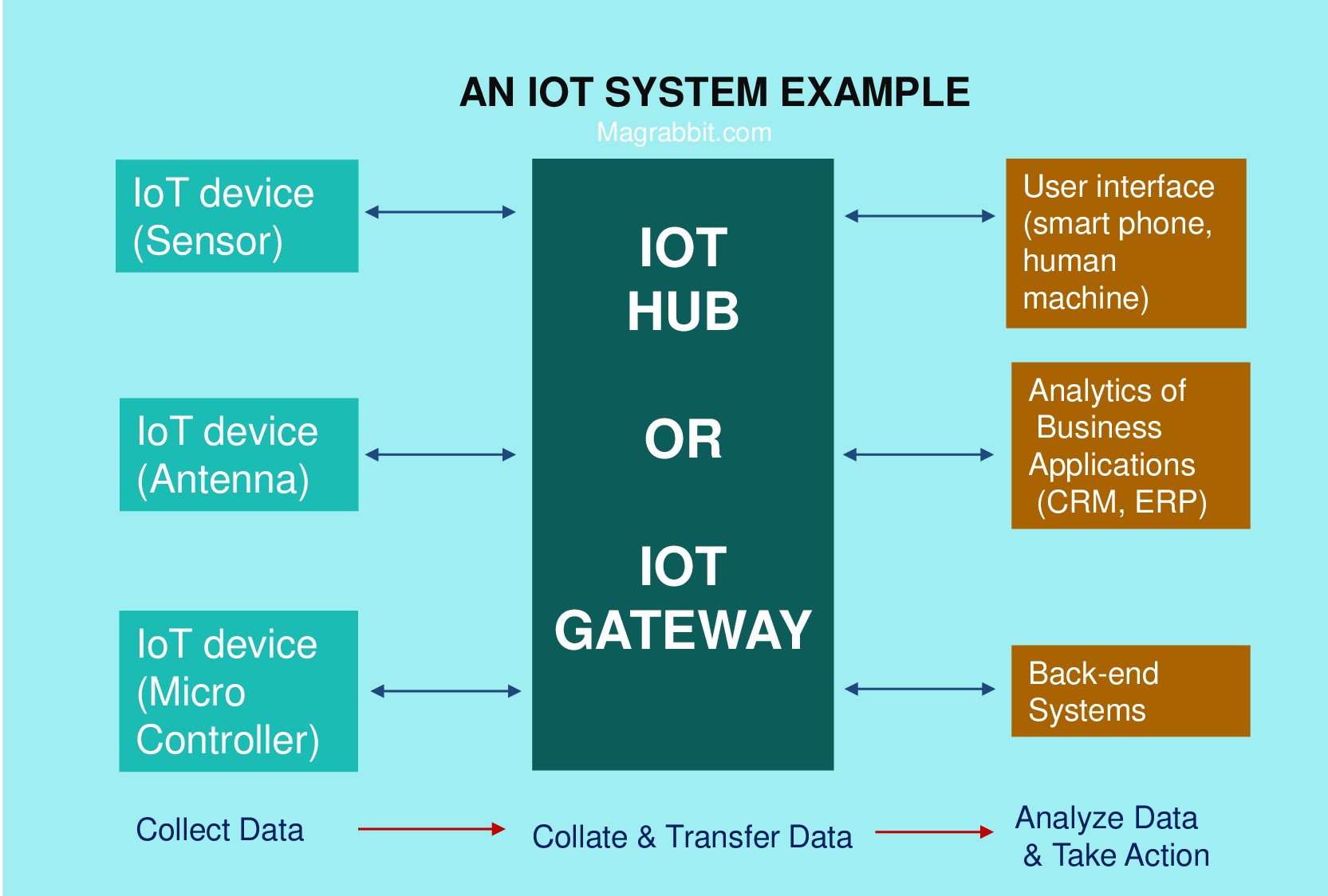
An example of how an IoT system works from collecting data to taking action
An IoT system includes web-enabled connected devices that utilize embedded technologies such as processors, sensors and communication equipment to capture, transmit and respond on data they receive from their surroundings. IoT devices share the sensor data they are gathering by connecting to an IoT gateway or other edge nodes where data is either sent to the cloud for analysis or analyzation locally.
Such systems often interact with other similar devices and operate on the input they obtain from each other. Much of the research is performed without human interference by the machines, but humans may communicate with the devices — for example, set them up, send them directions or view the data.
The synchronization, networking, and collaboration protocols that are used for these web-enabled devices rely largely on the particular IoT applications deployed.
IoT may also leverage Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning to further accelerate and dynamize data processing processes.
The reasons why IoT is important:
IoT allows people to live and function better and to take greater ownership of their lives. IoT is important for the industry, and to providing smart devices to automate homes. IoT gives companies a realtime look at how their systems really work, providing insights into everything from machine performance to supply chain and logistics operations.
IoT lets businesses automate processes and reduce labor costs. It also reduces duplication and increases service quality, making it less costly to make and supply products, as well as keeping consumer purchases open.
Therefore, IoT is one of the most important technologies of everyday life, and as more businesses realize the potential of connected devices to keep them competitive, it will continue to pick up steam.
Organizations benefits from IoT
IoT gives organizations multiple benefits. Some of the benefits are specific to an industry, and some are applicable across multiple industries. Some of IoT's common benefits allow undertakings to:
IoT provides companies with the tools they need to improve their business strategic plan and encourages them to rethink how they approach their businesses.
IoT benefits farmers by making their jobs easier. Sensors can collect data on rainfall, humidity, temperature, soil and other factors that would help automate farming techniques.
Another aspect that IoT can assist with is the opportunity to track activities involving infrastructure. For example, sensors may be used to track activities or adjustments taking place inside concrete structures, bridges and other facilities. It provides advantages, such as expense reduction, time saves, improvements in the efficiency of the process and paperless process.
Smart cities can help citizens cut waste and energy consumption on a broader scale using IoT. A home automation company may use IoT to control and manage in-build mechanical and electrical systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages of IoT
IoT's advantages :
IoT disadvantages:
Real-life uses of the Internet of Things
There are various real-world uses of the IoT. IoT implementations include transportation, telecommunications and electricity.
For example, in smart homes fitted with smart thermostats, smart appliances, connected heating, lighting, electronic devices can be remotely operated through computers and smartphones.
Devices with sensors and applications will capture and interpret users’ data and transmit notifications to other app-related technology to make things simpler and more convenient for consumers.
Wearable tools are often used for public protection — for instance, enhancing reaction time for emergency responders during crises by offering automated routes to a venue or monitoring vital signs from building staff or firefighters at life-threatening locations.
IoT provides numerous benefits in healthcare, including the potential to track patients more closely by an interpretation of the produced results. Hospitals often use IoT systems to complete tasks such as managing inventories for both pharmaceuticals and medical devices.
For example, smart buildings can reduce energy costs by using sensors that detect how many occupants are in a room. The temperature may be changed automatically — for example, if sensors noticing a meeting room is packed, switch the air conditioner on, or turn down the heat if anyone in the workplace has gone home.
In agriculture, IoT-based smart farming systems may help track crop fields with linked sensors such as sunlight, heat, temperature, humidity and soil moisture.
IoT devices and applications in a smart community, such as smart streetlights and smart meters, will help ease traffic, save electricity, track, fix environmental issues and enhance sanitation.
IoT security and privacy issues
IoT protection and IoT privacy are listed as major issues because of its increased surface area of attack. IoT links billions of machines to the Internet and requires the usage of billions of data modules, that must all be protected.
Since IoT systems are tightly related, the only thing a hacker has to do is leverage one bug to access all of the info, rendering it useless. Manufacturers that don't frequently upgrade their gadgets — or at all — make them exposed to cybercriminals. Hackers aren't the only danger to stuff on the Internet. Safety is another major problem for IoT users. For starters, businesses manufacturing and selling consumer IoT products may use such products to capture and sell personal data from consumers.
IoT presents a challenge to vital assets, including power, transportation and financial services, above leaked personal info.
info@magrabbit.com
sales@magrabbit.com
Compiled from several trustworthy sources